by Susan Dean | Feb 6, 2018 | Earth Science
Water Experiments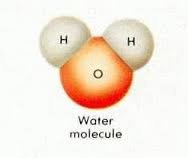
1. Put a dry pinecone in a bucket of water and observe what happens.
2. Put fresh water in one jar and salt in another and gently drop a raw egg into each. The one in salt water floats. If an egg is old it will stand u or float on fresh water. Salt water has a higher density.
3. Let them observe a water vortex that forms in the sink or tub when you let the water out. Kids love the vortex they can make with the vortex maker – a connector between two plastic bottles.
4. Freeze some water in a plastic cup after marking the water level. Measure it afterwards to see how it expanded. Water expands by 1/9th its volume when it freezes.
5. Spray some water on the chalkboard to observe water evaporation. Blow a fan on one spot to see how moving air accelerate the evaporation of water.
6. Put a drop of food coloring in a glass of water and observe how the molecules move through the water to color it.
7. Dissolve different substances in water to show it’s great ability as a solvent (salt, sugar, corn starch, instant coffee or chocolate etc..)
8. Put some ice in a bowl of water to show that water floats on top of itself when frozen (show picture of an iceberg).
9. Let a jar of saltwater sit to evaporate and see if the salt evaporated out.
10. Put some water colored with food coloring in a vase of white flowers and see how plants drink water.
11. Teach them “The Water Cycle” song and “Water Going Down the Drain”
12. Put some ice in a can with some salt and observe the formation of dew on the outside.
13. When water evaporates it takes heat with it. Put some water on the back of your hand and blow on it. You will notice a different feeling when you blow on the dry hand.
14. Check out the weight of a gallon of water.
15. Test what sinks or floats in water.
A GOOD EXAMPLE OF SURFACE TENSION

by Susan Dean | Feb 6, 2018 | Earth Science
COLORED SANDS OF THE SAHARA DESERT

James Hutton is the father of geology. He envisioned the cyclical nature of geologic processes. Geology is a science that deals with the history of the earth and its life especially as recorded in rock. It is the study of earth’s structure and the forces that produce them, including earth tectonics.
There are 92 elements naturally occurring on earth. An element has only one kind of atom. Elements are created in the stars. Some elements are attracted to each other and some are not. When 2 atoms of hydrogen get very hot and combine into 1 atom of helium (dry ice), neutrons are released as energy causing more heat. In nuclear fusion, 2 atoms fuse together to form a heavier element. When nuclear fusion takes place in a cloud of hydrogen, so much energy is released a star is born. If the reactions are uncontrollable, the star explodes in a supernova and elements spew into space.
99% of the mass of the universe is made of 2 elements – hydrogen and helium.
99% of the mass of the earth is made of 8 elements: iron, oxygen, calcium, silicon, magnesium, aluminum, sulfur, nickel.
Elements in the human body:
oxygen 65%
carbon 17.5%
Hydrogen 10.2%
nitrogen 2.4%
calcium 1.6%
all others 3.3%
Gold is one of the few elements found in a pure state. Its most common occurrence is in quartz. Bismuth is the heaviest element not radioactive. There are 6 elements that cannot be combined with other elements: Helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. They always exist as single atoms.
A mineral is made of one or more chemical elements. Chemicals in a mineral account for its softness, shine, and other noticeable properties. Anything not a plant or animal is a mineral. Many things are made of minerals: houses, cars, glass, dishes, pots, knives, paint, bridges, signs, jewelry, furniture, clay, chalk, talc powder, cement, sidewalks, roads, pipes, and wires. Almost all minerals are found in a solid state but water.
WATER is a liquid mineral. Ice is a water crystal. Flint is one of the oldest minerals used by man. Salt is a mineral known as Halite that comes from the sea. People used salt and turquoise for money long ago. We eat minerals in our food: liver = iron, milk and cheese = calcium, salt = iodine, beans & peas = copper and manganese, fish = phosphorus.
Of the rock forming minerals the most common are quartz, feldspar, & mica. Quartz is the most important rock-forming mineral and has many colors. Ex. smoky quartz, citrine, amethyst, rose.
Metals are minerals that have certain properties like shiny and good conductor of heat and electricity, and can be pressed, hammered, and bent such as gold, copper, silver, iron, aluminum and steel (foil, tin and aluminum cans). A television has 35 minerals and the telephone has 40.
Gemstones are minerals that have beauty, hardness, rarity, and sometimes translucence. Of the gemstones, emerald and diamond are the most rare.
Rock is an aggregate of one or more minerals and they are the building blocks of the earth’s crust Many rocks contain silica (SiO2); a compound of silicon and oxygen that forms 74.3% of the Earth’s crust. This material forms crystals with other compounds in the rock. The proportion of silica in rocks and minerals is a major factor in determining their name and propertiesThe types and abundance of minerals in a rock are determined by the manner in which the rock was formed.. Rocks are geologically classified according to characteristics such as mineral and chemical composition, permeability, the texture of the constituent particles, and particle size. Most rocks contain about 6 minerals. A mineral is homogenous. (molecules of every mineral are arranged in a particular crystalline structure that dictates its shape.)
MOON ROCKS
 THE MOST VALUABLE ROCKS ON EARTH!
THE MOST VALUABLE ROCKS ON EARTH!
The Rock Cycle is the dynamic transitions through geologic time among the three main rock types: sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous. The Rock Cycle explains how the three rock types are related and how processes change one type to another over time. The cycle is driven by plate tectonics and water and temperature.
Rocks are many colors, sizes, and shapes and are found everywhere: pebbles, stones, boulders, mountains, and islands. They can be round, square, spiked, plated, smooth, rough, hard or soft. Some have eyes. Some have stars. They may be clear, black, or mixed colors, magnetic or radioactive. Quartzite is metamorphosed sandstone found in the high Blue Ridge Mts. It is the most durable rock known. Quartz consists of rock crystals such as rose, amethyst, tigers eye.
ROCK QUARRIES are areas where rock is mined. Ex. Granite, sandstone, marble, limestone. Gravel is crushed rock. Rock is eroded by wind and water continually and is created through volcanoes. Famous rocks are: the Grand Canyon, Clingmans Dome, the Petrified Forest, and Caesars Head
The cryptocrystalline group of rocks has a crystalline structure so fine you cannot see particles under a microscope. It includes agate, bloodstone, carnelian, onyx, moss agate, chert, flint, and jasper.
Schistocity is how a rock breaks. Some crumble, flake, or break in one direction. Some rocks fluoresce and glow under ultraviolet light. Ex.willemite, calcite, hardystonite, autunite, scheelite, hydrozincite, semi-opal, wernerite
Moon rocks are the most expensive rocks ever collected and are a symbol of a dream come true. They are lumps of blackish rock. There is no trace of fossils or oceanic matter on the moon. Moon rock mineral composition is similar to earth rocks but differently combined. There are 2 types of rock on the moon: igneous rocks and breccias. There is the highest content of elements with high melting points and few with low melting points (opposite on earth). They are a mixture of pieces of iron, meteorites, igneous rock, and glassy fragments. The soil is a high content of nickel, cadmium, zinc, silver, gold, and copper. The soil has a high content of meteorite chips formed 3-7 billion years ago.
IGNEOUS ROCKS are formed from fire deep in the earth. Magma is molten rock. Magma is the Greek word for dough. Hot lava spews forth from volcanoes. The plutonic
rocks solidify deep in the earth’s crust. Basalt and granite crystallize in magma. Some minerals are formed by direct crystallization from a gas. Sulfur crystallizes from a gas released at volcanic vents around hot springs and forms a powdery crust or large crystals, burns with an unpleasant odor, is used in insecticides and to make paper, matches, and explosives.
Granite is quartz, feldspar, and mica and is the most common igneous rock. It is molten rock that cools underground before it gets to the surface. Huge rocks are created this way and can be red, pink, yellow, and brown. A good place to find them is around old volcanoes.
Iron pyrite is a cube made of iron and sulfur. It forms good crystals, comes from the decay of animal and vegetable matter, forms nodules in shale and chalk, occurs in irregular masses, and is pale brass yellow and sparks when struck.
Galena is lead and sulfur, the most common mineral with lead, cubes splits easily and are large masses in limestone. It is heavy and shines silver gray.
Magnetite is iron and oxygen. The crystal is the same as diamond and it is strongly magnetic. ex. Lodestone (points north.)
Hematite is Greek for blood. Kidney ore makes a red streak and is the most important source of iron. It is widespread in sedimentary rocks and causes the red color of many rocks.
Corundum has 6-sided barrels and spindles such as ruby, sapphire and 6 rayed stars.
Feldspar occurs in almost all igneous rocks and is white, light pink and green. It is changed to clay by wind and water. We find granite with pink feldspar or white feldspar.
Almandine and staurolite are plutonic. Staurolite is found at Mineral Bluff, Georgia and in Virginia.
Lava is a common igneous rock. If lava cools fast it forms obsidian that looks like glass. Other igneous rocks are diorite, felsites, basalt, pumice, granite, and feldspar.
Pyrolucite consists of manganese and oxygen and forms fernlike shapes in sedimentary rock or thin radiating crystals that form nodules at the bottom of the sea with copper, iron, and nickel.
Stone Mt. in Georgia is an example of a rock formed at great depths. Uplifts and erosion have made it visible. The following mountains were formed from slow folding glaciers: Swiss Alps, Appalachians, Atlas, Urals, Rockies, and Himalayan. Volcanic domes and cones are faulted and folded peaks. Faulted mountains rise and fall. Ex. Kilimanjaro, Fujiyama, Vesuvius, Etna. Dome Mt. of Utah is an example of volcanism but it does not erupt.
SEDIMENTARY rocks are mostly made under water from rock, sand, and mud. The top layer puts pressure on the bottom and they change into sandstone, limestone, shale, marble, slate, schist, coal, conglomerate, and gypsum (chalk.)
One finds limestone where land was once under water and it forms only under water.
Conglomerate is made in old streams and riverbeds. Sandstone can be gray, yellow, red, and brown. Shale is created from fine silt and mud and has the odor of wet earth. Ex. Limestone, sandstone, mudstone, dolomite, salt, coal. Stalactites in caves are sedimentary rock formation
METAMORPHIC rocks are formed from heat and pressure changes 40 miles below the earth’s surface in 1% of the earths crust. Limestone turns to marble.
Shale turns to slate. Schist is from mudstone and shale and sparkles with mica.
Serpentine is green and slippery to the touch as if covered with wax or soap. Quartzite is formed from sandstone. The most famous metamorphic rock is marble Ex. Talc, marble, serpentine, quartzite, slate, schist.
CRYSTALS The most solid substances are crystalline and have a shape. Diamond as a natural crystal has no sparkle.
There are 6 Systems of crystals:
- Cubic = halite
- Orthorhombic = sulfur
- Tetragonal = rutile
- monoclinic = epppidote
- Hexagonal = calcite
- triclinic = amazonite
How to identify rocks: Where did it come from? How hard is it? We use the hardness scratch test.
Hardness scale:
Talc is metamorphic and the softest
Gypsum is sedimentary and colorless or white. Ex. plaster of parries, chalk
Calcite is colorless or white and found in all groups. Ex. Iceland spar
Fluorite is colorless or many colors
Apatite yellow is most common
Feldspar is one of the most common minerals on earth and turns to clay
Quartz is most common
Topaz
Corundum ex. Ruby, sandpaper
Diamond is the hardest mineral, is rare and formed from compressed carbon.
Use a streak plate to identify rocks. Some make a colored streak. You can identify them by origin, hardness, streak, and weight.
Fossil is a Latin word meaning “dug up”. Fossils animals and plants are found in sedimentary rock such as limestone. Wood becomes petrified,
Meteorites – Gibeon in 1838 fell in Namilua Africa. Henburg fell in Australia and caused 13 craters in 1½ sq. miles in central Australia. Canyon Diablo caused the Arizona meteor crater and was the first meteor crater identified on earth. An iron meteor fell 40,000 years ago. It was 80 ft in diameter and weighed 63,000 tons. The impact crater is 4,200 feet in diameter. The floor is 750 feet below the rim. 150 impact craters have been discovered around the world
To think about:
Tools you would need for mining, a rock hound, rockslide, rock climbing, between a rock and a hard place, faith as a stone in a box, honey from the rock, rock and roll! Get the lead out of your shoes
PUMICE IS THE ONLY ROCK THAT FLOATS ON WATER!

112 ELEMENTS ILLUSTRATED
Death Valley


by Susan Dean | Feb 6, 2018 | Earth Science

Matter is everything that you can see touch and feel.
It takes up space, has mass, and can be dead or alive.
The forms of matter are SOLID, LIQUID, GAS and PLASMA
All matter is made of particles called ATOMS
ATOMS – “ATOMA” means indivisible. PROTONS and NEUTRONS form the NUCLEUS.
ELECTRONS spin around the nucleus. Atoms differ only in the # of protons in the nucleus and # of electrons spinning around it. This is what determines whether it is a solid, liquid, or gas. Hydrogen is the lightest element. Uranium is the heaviest.
Molecules are made of 2 or more atoms and are always in motion. Compounds are atoms joined together of 2 or more kinds of atoms = H2O
CHARACTERISTICS OF A SOLID:
1. molecules are very close together and jiggle in place
2. Keep a definite shape and size
3. Most molecules are arranged in patterns like crystals
4. They change when a force acts upon them
5. They have physical the properties of color, texture, hardness, odor, luster, melting & freezing points, malleability, and ductility.
Mass is the amount of matter an object contains. / The amount of force to move a weight is the gravitational force and depends on the distance from gravity. If you weigh 100 on earth you would weigh 16 lbs. on the moon but the mass remains the same. Find the center of gravity with a straw.
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIQUIDS:
1. The atoms are farther apart and slide around each other allowing flow.
2. Have no definite shape but moves freely, but have a definite size.
3. Exhibit capillary action. Water is pulled into spaces uphill as molecules exhibit cohesion (molecules have a strong attraction for each other) Water moves from soil into roots by the method of cohesion.
4. Has surface tension (float a needle or paper clip on water)
5. Some liquids are lighter and less dense than others.
Natural Liquids are water, petroleum, blood, lava, sap, and honey.
You can layer liquids. Oil dissolves in alcohol.
CHARACTERISTICS OF GAS:
1. Molecules are far apart moving fast and bouncing off one another
2. Has no definite shape but moves freely
3. Flows through neon signs
4. Expands when heated
5. INVISIBLE
6. Most are odorless
7. It contracts when cooled

When matter expands it gets bigger and when it contracts it “usually” gets smaller. Matter usually contracts when cooled and expands when heated. Water is one example of a liquid than expands and gets larger when frozen. Hoses can be ruined if water left in them freezes or water pipes may freeze and burst.
A Thermometer is often used to measure the temperature of the home or food when cooking. The temperature is also a gage for when to plant.
An ELEMENT consists of ONE KIND OF ATOM. MANDELEV created the periodic table of elements. BOYL identified 100 kinds of elements. There have been a few more discovered recently. Mass = bulk or quantity. Adhesion is when the molecules are attracted to surface molecules of other substances as water clings to the teeth of a comb.
Water is the only element found in all three states in nature.
Gas as fog, clouds, steam, mist
Solid as arctic ice, hail, icicles, sleet, snow, frost
Liquid as rain, ocean, dew, rivers, ponds, ground water and puddles.
We use all three states of water in everyday life. Living things are mostly made of water!
Solid + heat = liquid . . . liquid + cold = solid liquid + heat = gas
CO2 under pressure and then cooled turns the gas to dry ice. Dry ice melts to a gas. SUBLIMATION is when a solid is turned to gas
If warm air is cooled or meets cold air it forms condensation.
Different liquids evaporate into a gas at different rates (paint alcohol, water, and vinegar on a chalkboard)
Epsom salts and water, plus add a little ammonia, and it turns white forming a precipitate.
Teach the water cycle song about Evaporation, Condensation, and Precipitation
Experiments:
1. CO2 from borax and vinegar to blow up balloon
2. Two liquids combine to a solid in slime
3. Thermometer goes up from heat
4. Teach them the Molecule dance
5. Water song
6. Capillary action with different kinds of paper strips
7. Layer liquids

Plasma is an electrically neutral medium of unbound positive and negative particles ( the overall charge of a plasma is roughly zero). Although they are unbound, these particles are not ‘free’ in the sense of not experiencing forces. When the charges move, they generate electric currents with magnetic fields and they are affected by each other’s fields. This governs their collective behavior with many degrees of freedom. A definition can have three criteria:
The plasma approximation: Charged particles must be close enough together that each particle influences many nearby charged particles, rather than just interacting with the closest particle (these collective effects are a distinguishing feature of a plasma). The plasma approximation is valid when the number of charge carriers within the sphere of influence (called the Debye sphere whose radius is the Debye screening length) of a particular particle is higher than unity to provide collective behavior of the charged particles. The average number of particles in the Debye sphere is given by the plasma parameter.
Bulk interactions: The Debye screening length is short compared to the physical size of the plasma. This criterion means that interactions in the bulk of the plasma are more important than those at its edges, where boundary effects may take place. When this criterion is satisfied, the plasma is quasineutral.
Plasma frequency: The electron plasma frequency (measuring plasma oscillations of the electrons) is large compared to the electron-neutral collision frequency (measuring frequency of collisions between electrons and neutral particles). When this condition is valid, electrostatic interactions dominate over the processes of ordinary gas kinetics.
Ranges of parameters
Plasma parameters can take on values varying by many orders of magnitude, but the properties of plasmas with apparently disparate parameters may be very similar. The following chart considers only conventional atomic plasmas and not exotic phenomena like quark gluon plasmas:
Terrestrial Plasma:
Lightning
St. Elmo’s fire
Upper-atmospheric lightning (Blue jets, Blue starters, Gigantic jets, ELVES)
Sprites
The ionosphere
The plasmasphere
The polar aurorae
Some flames
The polar wind, a plasma fountain
Celestial plasma:
The Sun and other stars
(plasmas heated by nuclear fusion)
The solar wind
The interplanetary medium
(space between planets)
The interstellar medium
(space between star systems)
The Intergalactic medium
(space between galaxies)
The Io-Jupiter flux tube
Accretion discs
Interstellar nebulae
Cometary ion tail
by Susan Dean | Feb 6, 2018 | Animals, Earth Science

The study of fossils is called Paleontology. Fossil means “to dig”. Fossil records show us about life that was unable to adapt and the remains of prehistoric life. Fossils are dug up clues in rocks. If dead bodies are buried in sediment, the hard parts remain such as bones or teeth, and shells.
The Rockies, Alps, and Andes were once under water. Most fossils are made in lakes or seas. The strata are layers of sedimentary rock. The bottom layer of strata is the oldest. The oldest rocks known are 3000 million years old. In 1749 – 250 years ago a unicorn was reconstructed from fossil bones.
To become fossilized a plant or animal must:
1. Usually have hard parts as bone, shell, or wood
2. Be buried quickly to prevent decay
3. Be undisturbed through the process
Sometimes whole animals are preserved. Fossils have shown us that the early elephants were more like hogs. In Siberia and Alaska fossil mammoths about 25,000 years old have been found in frozen ground. Insects have been found in amber (the fossilized sap from trees). Leaves or small marine animals have been buried in mud that hardens to shale and a thin film of carbon remains outlining the form and preserving it.
Silica, iron, and lime are deposited in fossils. Petrified wood is mostly silica. In some fossils the life material has dissolved away and only a cavity remains. If substances fill in the cavity a cast will be formed. Gastroliths that dinosaurs used in digestion have been found. Rocks are formed from mud, sand, and clay in the seas, lakes, caves, deserts, and river valleys. Sedimentary rock contains almost all the fossils found. Rainfall, wind, running water, and evaporation change the surface of the earth. Erosion produces the sediments from which sedimentary rocks are formed.
SEDIMENTARY rock:
Limestone in warm shallow seas is often found w/fossils
Shale from silt and clay
Sandstone in deserts and shallow water with ripple marks and mud cracks
Fossils are a source of coal, oil, and lime. Fossils allow us to plot geography and reconstruct life and history. They are clues to the earth’s past climates and they map rock formations.
Fossil corals, brachiopods, bones, wood and ammonites have been found that lived millions of years ago. Rocks have been found pitted with raindrops, footprints, ripples from waves, and imprints of plants. Wood may become petrifies and turned to stone, or a fossil may be cast as a clam. Coprolite or fossilized excrement has been found. Some fossils are found in AMBER (pine resin) with insects inside. In the ice of Siberia, a wooly mammoth was found preserved.
In the Grand Canyon we can see the strata (layers) of rock. Erosion of rock occurs from weather and plants and water. Rocks can be crushed into soil.
Fossils have been found in mines, where roads or railroads were cut through or canals built, at beaches, rivers and in mountains and gorges.
Paleontologists have discovered dinosaur eggs as big as beach ball, horn coral and coprolites from the Devonian period, a dinosaur tooth from the Triassic age, fossil barnacles, arthropods, gastropods, trilobites, brachiopods, sea urchin, ammonites, worms, an elephant tooth of a mastodon & mammoth, and a large scallop from the Miocene age.

Ray Chapman Andrews developed fossil expeditions. Some were so big that problems arose about how to remove fossils from the ground and carry them home. It wasn’t as easy as just finding them. They wanted to preserve them. There weren’t many maps then.
What to take on a fossil expedition:
Field glasses, cameras, notebook, map, crowbar, pick, shovels, hammer, chisels, wire brush, plaster and shellac for repair.
Draw a chart of the arrangement of bones in rock
Take pictures
Number the bones before removing them
Fossils are pried out of the ground, covered with thin wet paper, covered with plaster – like a plaster cocoon for protection. They may have to be lifted with a block and tackle on a tripod if they are very large. They may be crated and cushioned with wood wool or a soft material when ready for a journey. When they arrive, the cocoon is soaked off, splints removed, paper comes away and there is the bone! The fossil is cleaned on one side then the other on a bed of fine sand. Broken pieces are mended, missing parts restored and inserted and then the experts study the fossil. They may decide to mount the fossil. Fossils are given International Greek or Latin names to not be misunderstood,


Trilobites are one of the most universally recognized fossils. Trilobites roamed the sea floors from 520 million years to 250 million ago. Trilobites were a wonderfully diverse group of arthropods that came in various sizes from less than an inch to several feet in length. Some of them can have a very exotic look to them. The Biggest Trilobites – Isotelus rex is the largest known species of trilobite. It was found in northern Manitoba.
This humongous arthropod measures about 28 inches (72 centimeters) long. Isotelus rex is now on display at the Manitoba Museum in Winnipeg.
Ammonite
 Cephalopod is the name given to the Squids and Octopus. Ancient Cephalopods often had hard shells that could be straight or spiral and came in elaborate shapes, sizes, designs and colors. They varied in sizes of less than 1/4 in diameter to several feet in diameter. The three main groups of fossil cephalopod remains found are Nautiloids, Ammonites and Belimites.
Cephalopod is the name given to the Squids and Octopus. Ancient Cephalopods often had hard shells that could be straight or spiral and came in elaborate shapes, sizes, designs and colors. They varied in sizes of less than 1/4 in diameter to several feet in diameter. The three main groups of fossil cephalopod remains found are Nautiloids, Ammonites and Belimites.
These ancient beauties lasted from about 400 million years ago to about 160 million years ago when they disappeared about the time the dinosaurs became extinct. The legacy they left behind are some of the most diverse and interesting fossils that can be found.
The largest ammonites – Titanites are often 2 feet (53 centimeters) in diameter. They are found in southern England and come from the Jurassic Period.
Pachydiscus seppenradensis sometimes reach a diameter of 6 ½ feet (2 meters). They are found in Germany from the Cretaceous Period.
Parapuzosia bradyi can be 4 ½ feet (137 centimeters) in diameter. They are found in North American, from the Cretaceous Period.
The Largest Nautiloids – The largest nautiloid on record is called Endoceras. It is from the Ordovician Period and has been measured up to 13 feet (3 ½ meters) long.
Earth’s Oldest Fossils – The evidence of microscopic life forms has been detected as old as 3,700 to 3,800 million years ago. This evidence was found in Isua greenstone in Greenland. There have been claims of evidence dating back as far as 3,850 million years ago but these are not universally accepted.
 The Oldest Fish Fossils – The oldest fish fossils on record were found at Chengjiang, in Yunnan Province, China. Two species have been found dating from about 530 million years ago. Haikouichthys ercaicunensis, and Myllokunmingia fengjiaoa, are recent finds. If verified these finds will rewrite the fish chapter of evolution.
The Oldest Fish Fossils – The oldest fish fossils on record were found at Chengjiang, in Yunnan Province, China. Two species have been found dating from about 530 million years ago. Haikouichthys ercaicunensis, and Myllokunmingia fengjiaoa, are recent finds. If verified these finds will rewrite the fish chapter of evolution.
Largest Dinosaur – Sauroposeidon may have been the largest dinosaur ever to walk the face of the earth. Scientists believe this gigantic dinosaur would have stood 60 feet tall (18 meters) and weighed 60 tonnes! Sauroposeidon means “earthquake god lizard”. This dinosaur may also hold the record for having the longest neck.
Biggest shark – Megalodon is estimated to have been 40 to 50 feet long and weigh 48 tons!
Oldest Fossil Beds – The oldest fossils of multicelled animals come from two places on earth. The Burgess Shale formation in Canada was long regarded as the oldest fossil bed. The Burgess Shale was formed about 530 million years ago during the Cambrian period. Many early Cambrian Period fossils have been found there. The Chengjiang Deposits of China are thought to be older than Canada’s Burgess Shale. The fossils are found near the town of Chengjiang, in the Yunnan Province of China. This area appears to be about 15 million years older than the Burgess Shale formation.
 Brachiopods are benthic (bottom dwelling), marine (ocean), bivalves (having two shells). They are considered living fossils, with 3 orders present in today’s oceans. They are rare today but during the Paleozoic Era they dominated the sea floors.
Brachiopods are benthic (bottom dwelling), marine (ocean), bivalves (having two shells). They are considered living fossils, with 3 orders present in today’s oceans. They are rare today but during the Paleozoic Era they dominated the sea floors.
Though they appear to be similar to clams or oysters they are not related. They are not even mollusks. They belong to the phylum Lophophorata and are related to bryozoans. Crinoids are unusually beautiful and graceful members of the phylum Echinodermata. This is the phylum that brings you starfish, sea urchins, and sand dollars. The crinoids are a breed apart however, they resemble an underwater flower. Some even have parts that look and act like roots anchoring them to the ocean floor. They are commonly called sea lilies. Their graceful stalks can be meters long. Other varieties have no stalks or root like parts. They are commonly known as feather stars. Unlike the sea lilies the feather stars can move about on tiny hook like structures called cirri.
Crinoids are alive and well and living in an ocean near you! They are some of the oldest fossils on the planet. The earliest come from the Ordovician Period.. The few species surviving into the Mesozoic Era thrived. Many new species evolved during this time including the ancestors of the present day class Articulata. These echinoderms were at their height during the Paleozoic era. They could be found all over the world, creating forests on the floor of the shallow seas of this time period.

 Carcharodon Megalodon was a giant shark that lived during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs of the Cenozoic Era, between 2 million and 16 million years ago. Little is known about these giant predators because all that remains of their existence are fossilized teeth. These giant shark teeth range in size from 3 inches long to 7 inches long. They are massive things that can be bigger than a man’s hand.
Carcharodon Megalodon was a giant shark that lived during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs of the Cenozoic Era, between 2 million and 16 million years ago. Little is known about these giant predators because all that remains of their existence are fossilized teeth. These giant shark teeth range in size from 3 inches long to 7 inches long. They are massive things that can be bigger than a man’s hand.
Spider captured in amber







by Susan Dean | Feb 1, 2018 | Earth Science
 Jeff Cox
Jeff Cox
We Are Water! Plants and animals are mostly made of water. I hold up the large paper mache molecule and ask children what it looks like. They usually guess Mickey Mouse! Water is called the “Mickey Mouse Molecule” because that’s what the molecule looks like. H2O is 2 hydrogen ears and oxygen head.
Water is the universal solvent. It is tasteless, colorless, odorless and unique. It is the only element on the earth found in all three forms – liquid, solid, and gas. Many things dissolves in water and it flows through everything that is alive. It is unique because when it freezes it grows bigger when most things shrink. The most important things we must have to stay alive are oxygen from the air and water to drink.
Water cycles. It evaporates into the air, condenses into clouds and precipitates out as rain, snow, sleet, hail, fog and dew. The sun is the driving force. Teach the water cycle song
This is a good time to talk about temperature and how molecules respond. When they are cold they pack closely and jiggle. When they heat up they start to slide around melting and then begin to move faster when they get hot and jump into the air. Children enjoy acting this out.
Examine pictures of clouds and lightning. Lightening is electrical flashes between the clouds and the earth. Thunder is made when the heat from the electrical flash makes the air expand quickly making the sound of thunder. You can illustrate this by popping a bag of air. The quick expansion of air makes the pop.
Talk about safety. Lightening is dangerous and they should take cover in a safe place like a building or car during a storm. Children know that it is very important for them to drink water and animals and plants are mostly made of water.
Materials: Hand drum, Mickey Mouse Molecule representing water, Hand out of the water cycle, Pictures of water, ice and clouds, water cycle chart, paper bag, misc. materials for doing other water experiments you choose.
Activities: Water cycle song, Act out the effect of temperature on molecules of water. Put a drop of food coloring in a bottle of water and watch the molecules disperse. Dissolve different substances in water ex. salt or sugar. Check buoyancy of different objects in water, a magnet goes through water, light goes through water. Check surface tension by floating a paper clip on the surface of a glass of water. , check the capillary action by putting the tip of a paper towel in a glass of water. Show examples of erosion, evaporation, condensation. Show difference in density of fresh and salt water with an egg. The egg floats in salt water. A straw appears bent in water. Explore the qualities of water through experiments, river books, rain sticks, and crystals.
Ice Halos Joshua Thomas, a photographer in Red River, New Mexico, was lucky enough to catch rainbow-like arcs and pillars of light blazing over a snowy landscape last week. This is caused by the collision of light and ice crystals high in Earth’s atmosphere.
Those frozen specks of water refract light in myriad ways to produce arcs, halos, and pillars of light. Air temperatures and the shape and arrangement of ice crystals fine-tune the phenomena that we see.
In the center of the image is a bright, vertical mass called a sun pillar. Cooler air temperatures boost the brightness of these phenomena. The circle of light ringing the pillar is a 22-degree halo. These halos are fairly common and are so named because they occur at a 22-degree angle from the sun. They’re created hexagonal ice crystals.
The glaring blob of light to the right of the pillar is called a sundog, the result of ice crystals that are only partly aligned with each other. Sundogs are fairly common.
The delicate strands of light winging out from the top of the sun pillar are tangent arcs. They’re formed when tube-shaped hexagonal ice crystals are oriented on their sides. The halos and arcs aren’t a harbinger of dangerous weather events.

“One of the most soothing sounds of nature is the laughter of falling water.”
WATER QUOTES:
When the well is dry we know the worth of water. Benjamin Franklin
The frog does not drink up the pond in which he lives. American Indian
Water has become a highly precious resource. There are some places where a barrel of water costs more than a barrel of oil. Lord Axworthy
Throughout the history of literature, the guy that poisons the well has been the worst of all villains.
“A lake is the landscape’s most beautiful and expressive feature. It is earth’s eye; looking into which the beholder measures the depth of his own nature.” Thoreau
The noblest of the elements is water. Pindar
“Water is the only drink for a wise man.” Thoreau
“When you drink the water, remember the spring.” Chinese proverb
“The cycle of life is intricately tied up with the cycle of water.” Jacques Cousteau
Frost Flowers – It is as beautiful as it is rare. A frost flower is created on autumn or early winter mornings when ice in extremely thin layers is pushed out from the stems of plants or occasionally wood. This extrusion creates wonderful patterns that curl and fold into gorgeous frozen petioles giving this phenomenon both its name and its appearance.



Lake Hiller

Blood Falls








 THE MOST VALUABLE ROCKS ON EARTH!
THE MOST VALUABLE ROCKS ON EARTH!












 Cephalopod is the name given to the Squids and Octopus. Ancient Cephalopods often had hard shells that could be straight or spiral and came in elaborate shapes, sizes, designs and colors. They varied in sizes of less than 1/4 in diameter to several feet in diameter. The three main groups of fossil cephalopod remains found are Nautiloids, Ammonites and Belimites.
Cephalopod is the name given to the Squids and Octopus. Ancient Cephalopods often had hard shells that could be straight or spiral and came in elaborate shapes, sizes, designs and colors. They varied in sizes of less than 1/4 in diameter to several feet in diameter. The three main groups of fossil cephalopod remains found are Nautiloids, Ammonites and Belimites. The Oldest Fish Fossils – The oldest fish fossils on record were found at Chengjiang, in Yunnan Province, China. Two species have been found dating from about 530 million years ago. Haikouichthys ercaicunensis, and Myllokunmingia fengjiaoa, are recent finds. If verified these finds will rewrite the fish chapter of evolution.
The Oldest Fish Fossils – The oldest fish fossils on record were found at Chengjiang, in Yunnan Province, China. Two species have been found dating from about 530 million years ago. Haikouichthys ercaicunensis, and Myllokunmingia fengjiaoa, are recent finds. If verified these finds will rewrite the fish chapter of evolution. Brachiopods are benthic (bottom dwelling), marine (ocean), bivalves (having two shells). They are considered living fossils, with 3 orders present in today’s oceans. They are rare today but during the Paleozoic Era they dominated the sea floors.
Brachiopods are benthic (bottom dwelling), marine (ocean), bivalves (having two shells). They are considered living fossils, with 3 orders present in today’s oceans. They are rare today but during the Paleozoic Era they dominated the sea floors.
 Carcharodon Megalodon was a giant shark that lived during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs of the Cenozoic Era, between 2 million and 16 million years ago. Little is known about these giant predators because all that remains of their existence are fossilized teeth. These giant shark teeth range in size from 3 inches long to 7 inches long. They are massive things that can be bigger than a man’s hand.
Carcharodon Megalodon was a giant shark that lived during the Miocene and Pliocene epochs of the Cenozoic Era, between 2 million and 16 million years ago. Little is known about these giant predators because all that remains of their existence are fossilized teeth. These giant shark teeth range in size from 3 inches long to 7 inches long. They are massive things that can be bigger than a man’s hand.














